1.数据提取的概念和数据分类
在爬虫爬取的数据中有很多不同类型的数据,我们需要了解数据的不同类型来又规律的提取和解析数据。
- 结构化数据:
json、xml- 处理方式:直接转化为
python数据类型
- 处理方式:直接转化为
- 非结构化数据:
HTML- 处理方式:正则表达式、
xpath、bs4
- 处理方式:正则表达式、
结构化数据
json

xml

非结构化数据
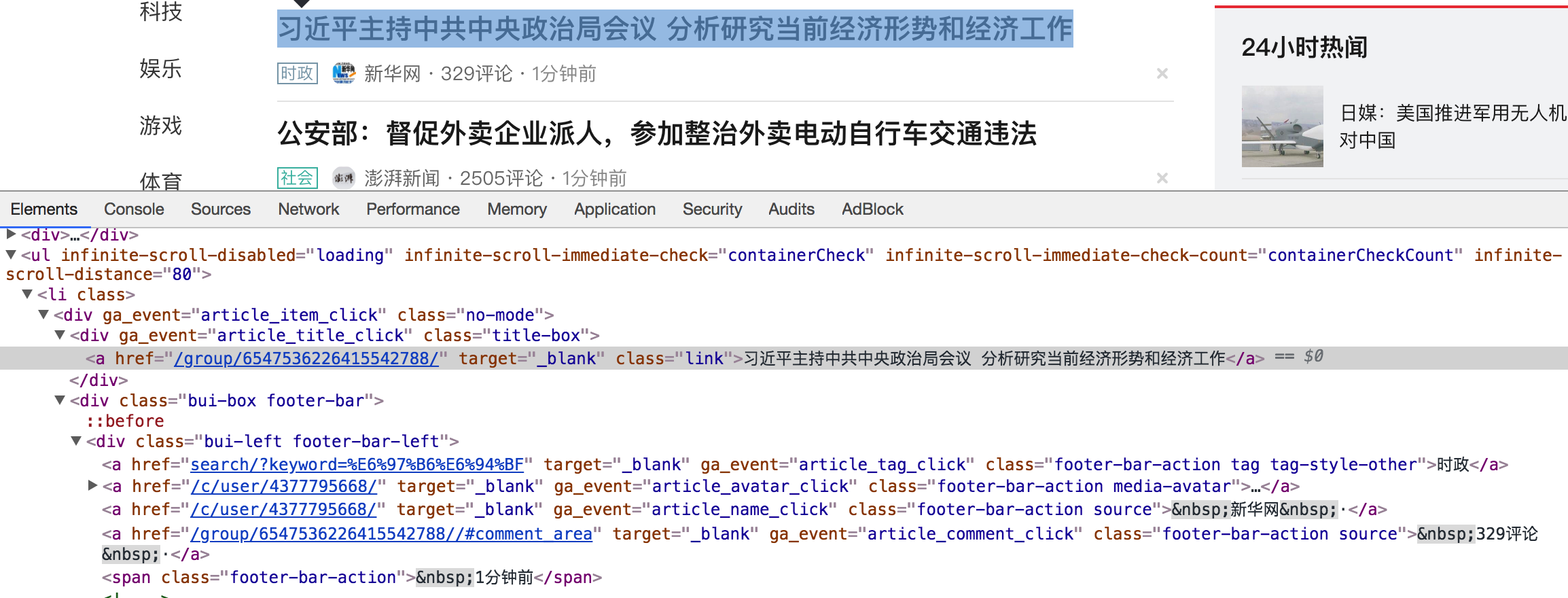
2.结构化数据提取 - JSON
什么是json
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,它使得人们很容易的进行阅读和编写,同时也方便了机器进行解析和生成,适用于进行数据交互的场景,比如网站前端与后端之间的数据交互。
json模块方法回顾
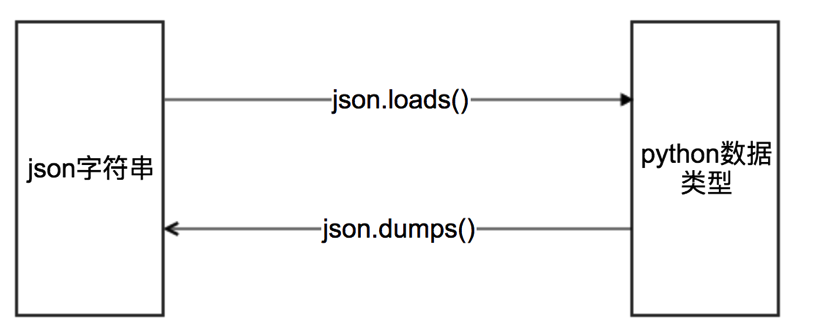
# json.dumps 实现python类型转化为json字符串
# indent实现换行和空格
# ensure_ascii=False实现让中文写入的时候保持为中文
json_str = json.dumps(mydict, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)
# json.loads 实现json字符串转化为python的数据类型
my_dict = json.loads(json_str)代码示例
import json
import requests
# 获取公告信息
url = 'http://www.cninfo.com.cn/new/disclosure'
# 定义请求头,模拟浏览器
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) "
"AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/117.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
}
# 定义表单数据
post_data = {
'column': 'szse_latest',
'pageNum': 1,
'pageSize': 30,
'sortName': '',
'sortType': '',
'clusterFlag': 'true'
}
# 请求json数据
r = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=post_data)
# 解码
json_str = r.content.decode()
# 把json格式字符串转换成python对象
json_dict = json.loads(json_str)
print(json_dict)
print("\n\n")
# 还可以使用json()
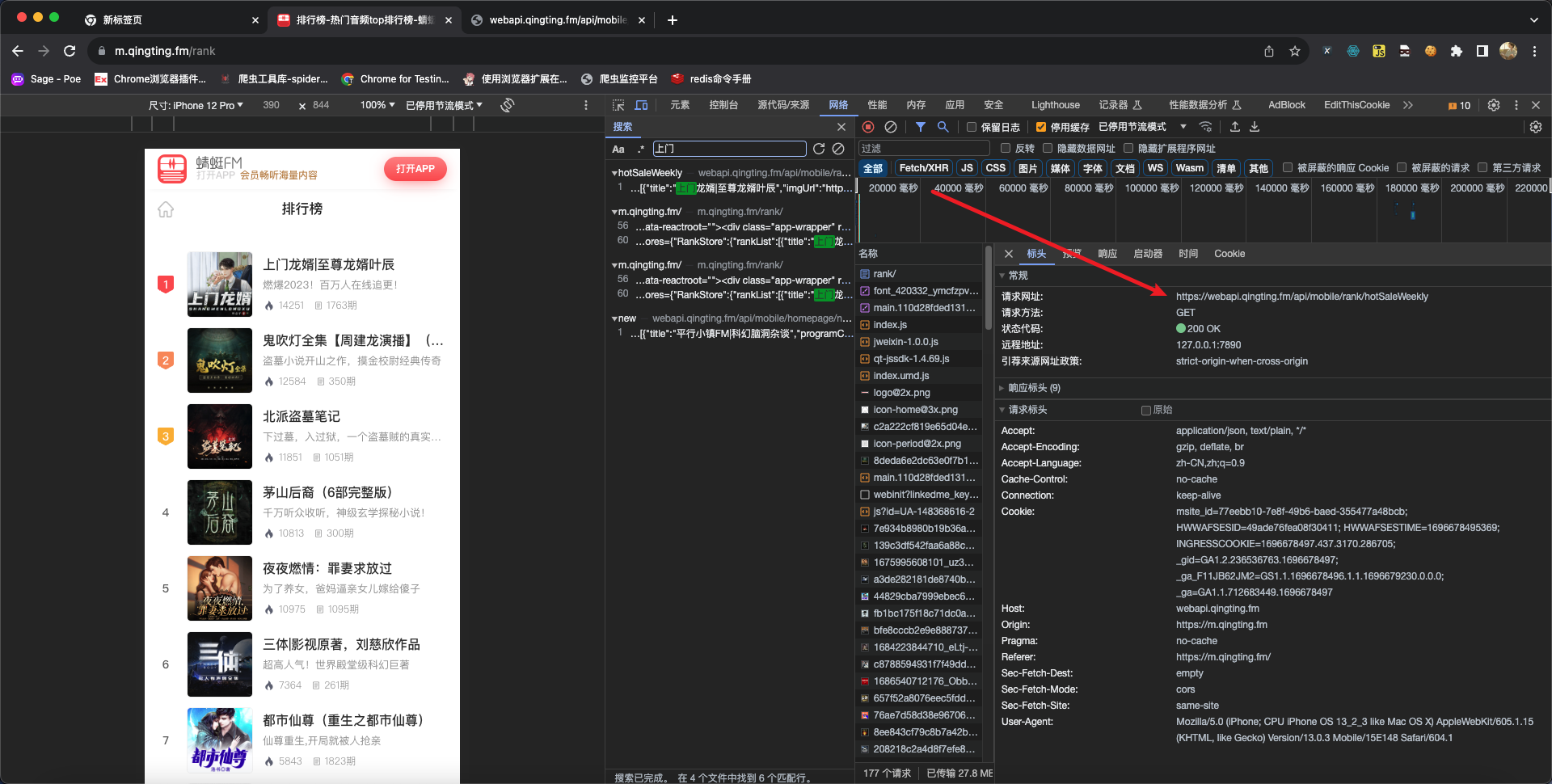
print(r.json())3.练习:蜻蜓FM排行榜信息
蜻蜓FM的首页url:https://m.qingting.fm/rank
代码示例:
import requests
url = "https://webapi.qingting.fm/api/mobile/rank/hotSaleWeekly"
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 13_2_3 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/13.0.3 Mobile/15E148 Safari/604.1"
}
r = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
print(r.status_code)
print(r.json())分析过程:
4.非结构化数据提取 - 正则
什么是正则表达式
用事先定义好的一些特定字符、及这些特定字符的组合,组成一个规则字符串,这个规则字符串用来表达对字符串的一种过滤逻辑。
正则表达式的常见语法
- 正则中的字符
- 正则中的预定义字符集
- 正则中的数量词
| 一般字符 | 匹配规则 | 表达式 | 完整匹配的字符串 |
|---|---|---|---|
. | 匹配任意除换行符\n外的字符 | a.c | abc |
\ | 转义字符,使后面一个字符改变原来的意思。如果字符串有字符*需要匹配,则可以使用\* | a\.c | a.c |
[...] | 字符集(字符类)。对应的位置可以使字符集中任意字符。字符集中的字符可以逐个列出,也可以给定范围:[abc]或[a-c]。第一个字符如果是^则表示取反:[^abc]表示不是abc的其他字符 | a[bcd]e | abe、ace、ade |
\d | 数字:[0-9] | a\dc | a1c |
\D | 非数字:[^\d] | a\Dc | abc |
\s | 空白字符:[<空格>\t\r\t\f\v] | a\sc | a c |
\S | 非空白字符:[^\s] | a\Sc | abc |
\w | 单词字符:[A-Za-z0-9_] | a\wc | abc |
\W | 非单词字符:[^\w] | a\Wc | a c |
* | 匹配前一个字符0次或者无数次 | abc* | ab、abccccc |
+ | 匹配前一个字符1次或者无数次 | abc+ | abc、abccccc |
? | 匹配前一个字符0次或者1次 | abc? | ab、abc |
{m} | 匹配前一个字符m次 | ab{2}c | abbc |
以上表格只是列出部分用法,对于其他用法请同学们善于利用搜索引擎查阅资料。
代码练习:
import re
string_a = '<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1">\n\t\t<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8">\n\t\t<meta content="always" name="referrer">\n <meta name="theme-color" content="#2932e1">'
ret = re.findall("<.*>",string_a)
print(ret)re模块的常见方法
pattern.match:从字符串开头找一个pattern.search:在字符串任意位置找一个pattern.findall:找所有- 返回一个列表,如果没有则返回一个空列表
re.findall('\d', 'zhi1zhi2')得到['1', '2']
pattern.sub:替换re.sub('\d', '_', 'zhi1zhi2')得到['zhi_zhi_']
re.compile:编译返回一个模型
P,具有和re一样的方法,但是传递的参数不同匹配模式需要传到
compile中pythonp = re.compile(r"\d") # 得到一个对象p, 可以用多次 p.findall("zhi1zhi2") p.findall("zhi1zhi100") # 下面的方式是每次匹配的时候都要写正则表达式 re.match(r"\d", "xxxx") re.match(r"\d", "yyyy")
匹配中文
在某些情况下,我们想匹配文本中的汉字,有一点需要注意的是,中文的 unicode 编码范围 主要在 [u4e00-u9fa5],这里说主要是因为这个范围并不完整,比如没有包括全角(中文)标点,不过,在大部分情况下,应该是够用的。
import re
title = '你好,hello,世界, 123'
pattern = re.compile(r'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+')
result = pattern.findall(title)
print(result)5.练习:爬取36kr新闻首页
代码示例:
import re
import requests
# 1. 爬取
url = "https://36kr.com"
# 模拟手机浏览器访问移动端页面
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 11_0 like Mac OS X) "
"AppleWebKit/604.1.38 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/11.0 Mobile/15A372 Safari/604.1",
}
r = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
# 2. 得到响应的内容
html = r.text
# 测试提取的页面数据
# print(html)
# 3. 通过正则表达式提取需要的数据
item_list = re.findall(r'<a class="item-info clearfloat" href="([^"]*).*?ellipsis-2">(.*?)</span>.*?</a>', html)
print("提取到的新闻个数:", len(item_list))
print(item_list)
for temp in item_list:
print(url + temp[0], temp[1])6.xpath语法
为什么学习xpath
在上一节学习中,我们使用的正则表达式来对爬取到的html数据进行处理,这种方式较为繁琐,而且有稍微有一点地方写错了,那么可能会导致匹配失败,从而提取数据失败。
一句话:使用正则提取数据,较为麻烦。所以才有了接下来学习XPath的原因。
什么是xpath
XPath (XML Path Language) 即XML路径语言,在最初时它主要在xml文档中查找需要的信息,而现在它也适用于HTML文档的搜索。
W3School官方文档:http://www.w3school.com.cn/xpath/index.asp
XPath可以很轻松的选择出想要的数据,提供了非常简单明了的路径选择表达式,几乎想要任何定位功能,XPath都可以很轻松的实现。
xpath节点
每个标签我们都称之为节点,其中最顶层的节点称为根节点。

辅助工具
Chrome浏览器插件:XPath HelperFirefox浏览器插件:XPath Finder
注意: 这些工具是用来学习XPath语法的,当熟练掌握XPath的语法后就可以直接在代码中编写XPath而不一定非要用此工具。
语法规则
XPath使用路径表达式来选取文档中的节点或者节点集。这些路径表达式和我们在常规的电脑文件系统中看到的表达式非常相似。
| 表达式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
nodename | 选中该元素 |
/ | 从根节点选取、或者是元素和元素间的过渡 |
// | 从匹配选择的当前节点选择文档中的节点,而不考虑它们的位置 |
. | 选取当前节点 |
.. | 选取当前节点的父节点 |
@ | 选取属性 |
text() | 选取文本 |
路径表达式
| 路径表达式 | 结果 |
|---|---|
bookstore | 选择bookstore元素 |
/bookstore | 选取根元素 bookstore。注释:假如路径起始于正斜杠(/),则此路径始终代表到某元素的绝对路径! |
bookstore/book | 选取属于 bookstore 的子元素的所有 book 元素 |
//book | 选取所有 book 子元素,而不管它们在文档中的位置 |
bookstore//book | 选择属于 bookstore 元素的后代的所有 book 元素,而不管它们位于 bookstore 之下的什么位置 |
//book/title/@lang | 选择所有的book下面的title中的lang属性的值 |
//book/title/text() | 选择所有的book下面的title的文本 |
查询特定节点
| 路径表达式 | 结果 |
|---|---|
//title[@lang="eng"] | 选择lang属性值为eng的所有title元素 |
/bookstore/book[1] | 选取属于 bookstore 子元素的第1个 book 元素 |
/bookstore/book[last()] | 选取属于 bookstore 子元素的最后1个 book 元素 |
/bookstore/book[last()-1] | 选取属于 bookstore 子元素的倒数第2个 book 元素 |
/bookstore/book[position()>1] | 选择bookstore下面的book元素,从第2个开始选择 |
/bookstore/book[position()>1 and position()<4] | 选择bookstore下面的book元素,从第2个开始取到第4个元素 |
//book/title[text()='Harry Potter'] | 选择所有book下的title元素,仅仅选择文本为Harry Potter的title元素 |
注意点: 在XPath中,第一个元素的位置是1,最后一个元素的位置是last(),倒数第二个是last()-1
语法练习
接下来对豆瓣电影top250的页面来练习上述语法:https://movie.douban.com/top250
选择所有的
h1下的文本xpath//h1/text()获取电影信息的
href属性xpath//div[@class='item']//div[@class='hd']/a/@href获取电影的评价人数
xpath//div[@class='star']/span[last()]/text()
总结
XPath的概述:XPath (XML Path Language),解析查找提取信息的语言xml是和服务器交互的数据格式和json的作用一致html是浏览器解析标签数据显示给用户XPath的重点语法获取任意节点://XPath的重点语法根据属性获取节点:标签[@属性 = '值']XPath的获取节点属性值:@属性值XPath的获取节点文本值:text()
7.使用lxml模块中的XPath语法提取非结构化数据
前面学习的XPath知识主要的作用是:学会怎样通过XPath语法找到需要的数据,想要在代码中使用Xpath进行处理,就需要学习另外一个新的模块lxml
模块安装
pip install lxml -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simplelxml的使用
- 使用
lxml转化为Element对象
from lxml import etree
text = ''' <div> <ul>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link1.html">first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a>
</ul> </div> '''
# 利用etree.HTML,将字符串转化为Element对象, Element对象具有XPath的方法
html = etree.HTML(text)
print(type(html))
# 将Element对象转化为字符串
handled_html_str = etree.tostring(html).decode()
print(handled_html_str)
- 使用
lxml中的XPath语法提取数据
提取a标签属性和文本
from lxml import etree
text = ''' <div> <ul>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link1.html">first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a>
</ul> </div> '''
html = etree.HTML(text)
# 获取href的列表和title的列表
href_list = html.xpath("//li[@class='item-1']/a/@href")
title_list = html.xpath("//li[@class='item-1']/a/text()")
for title, href in zip(title_list, href_list):
item = dict()
item["title"] = title
item["href"] = href
print(item)以上代码必须确保标签中的数据是一一对应的,如果有些标签中不存在指定的属性或文本则会匹配混乱。
from lxml import etree
text = ''' <div> <ul>
<li class="item-1"><a>first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a>
</ul> </div> '''
html = etree.HTML(text)
# 获取href的列表和title的列表
href_list = html.xpath("//li[@class='item-1']/a/@href")
title_list = html.xpath("//li[@class='item-1']/a/text()")
for title, href in zip(title_list, href_list):
item = dict()
item["title"] = title
item["href"] = href
print(item)输出结果为:
/Users/poppies/python_envs/base/bin/python3 /Users/poppies/Documents/spider_code/1.py
{'title': 'first item', 'href': 'link2.html'}
{'title': 'second item', 'href': 'link4.html'}
XPath分次提取
前面我们取到属性,或者是文本的时候,返回字符串 但是如果我们取到的是一个节点,返回什么呢?
返回的是element对象,可以继续使用xpath方法
对此我们可以在后面的数据提取过程中:先根据某个xpath规则进行提取部分节点,然后再次使用xpath进行数据的提取
示例如下:
from lxml import etree
text = ''' <div> <ul>
<li class="item-1"><a>first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a>
</ul> </div> '''
html = etree.HTML(text)
li_list = html.xpath("//li[@class='item-1']")
print(li_list)可以发现结果是一个element对象,这个对象能够继续使用xpath方法
先根据li标签进行分组,之后再进行数据的提取
from lxml import etree
text = ''' <div> <ul>
<li class="item-1"><a>first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a>
</ul> </div> '''
html = etree.HTML(text)
li_list = html.xpath("//li[@class='item-1']")
print(li_list)
# 在每一组中继续进行数据的提取
for li in li_list:
item = dict()
item["href"] = li.xpath("./a/@href")[0] if len(li.xpath("./a/@href")) > 0 else None
item["title"] = li.xpath("./a/text()")[0] if len(li.xpath("./a/text()")) > 0 else None
print(item)总结
lxml库的安装:pip install lxmllxml的导包:from lxml import etree;lxml转换解析类型的方法:etree.HTML(text)lxml解析数据的方法:data.xpath("//div/text()")- 需要注意
lxml提取完毕数据的数据类型都是列表类型 - 如果数据比较复杂:先提取大节点, 然后再进行小节点操作
8.练习:通过XPath提取豆瓣电影评论
要求
爬取豆瓣电影的评论,地址链接:https://movie.douban.com/subject/1292052/comments?status=P
提示
先在浏览器中使用插件XPath Helper进行XPath语法测试,效果如下:
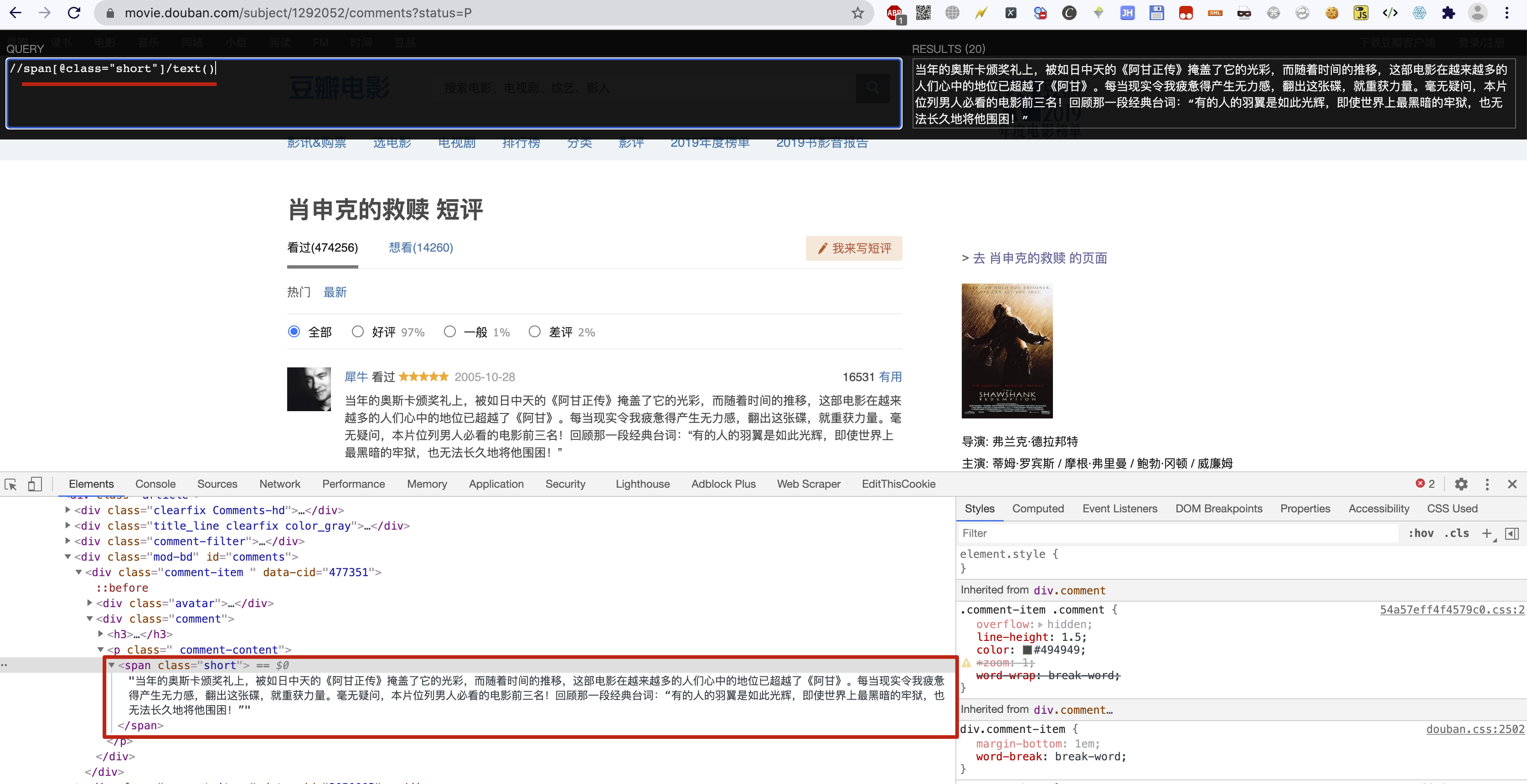
代码示例
import requests
from lxml import etree
"""
流程分析:
1. 通过requests发送请求获取豆瓣返回的内容
2. 将返回的内容通过etree.HTML转换为Element对象
3. 对Element对象使用XPath提取数据
"""
# 1. 通过requests发送请求获取豆瓣返回的内容
url = "https://movie.douban.com/subject/1292052/comments?status=P"
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/86.0.4240.183 Safari/537.36",
}
r = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
# print(r.text)
# 2. 将返回的内容通过etree.HTML转换为Element对象
html = etree.HTML(r.text)
# 3. 对Element对象使用XPath提取数据
comment_list = html.xpath('//span[@class="short"]/text()')
print("提取到的个数:", len(comment_list))
for comment in comment_list:
print(comment)
print('\n')9.jsonpath模块
JsonPath是一种可以快速解析json数据的方式,JsonPath对于JSON来说,相当于XPath对于XML,JsonPath用来解析多层嵌套的json数据。
官网:https://goessner.net/articles/JsonPath/
想要在Python编程语言中使用JsonPath对json数据快速提取,需要安装jsonpath模块
pip install jsonpath -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simplejsonpath常用语法

代码示例
import jsonpath
info = {
"error_code": 0,
"stu_info": [
{
"id": 2059,
"name": "小白",
"sex": "男",
"age": 28,
"addr": "河南省济源市北海大道xx号",
"grade": "天蝎座",
"phone": "1837830xxxx",
"gold": 10896,
"info": {
"card": 12345678,
"bank_name": '中国银行'
}
},
{
"id": 2067,
"name": "小黑",
"sex": "男",
"age": 28,
"addr": "河南省济源市北海大道xx号",
"grade": "天蝎座",
"phone": "87654321",
"gold": 100
}
]
}
"""
未使用jsonpath时,提取dict时的方式
"""
res = info["stu_info"][0]['name'] # 取某个学生姓名的原始方法:通过查找字典中的key以及list方法中的下标索引
print(res) # 输出结果是:小白
res = info["stu_info"][1]['name']
print(res) # 输出结果是:小黑
print("----------我是分割线----------")
"""
使用jsonpath时,提取dict时的方式
"""
res1 = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, '$.stu_info[0].name') # $表示最外层的{}, . 表示子节点的意思
print(res1) # 输出结果是list:['小白']
res2 = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, '$.stu_info[1].name')
print(res2) # 输出结果是list:['小黑']
res3 = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, '$..name') # 嵌套n层也能取到所有学生姓名信息,$表示最外层的{},..表示模糊匹配
print(res3) # 输出结果是list:['小白', '小黑']
res4 = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, '$..bank_name')
print(res4) # 输出结果是list:['中国银行']10.jsonpath练习
jsonpath对比XPath
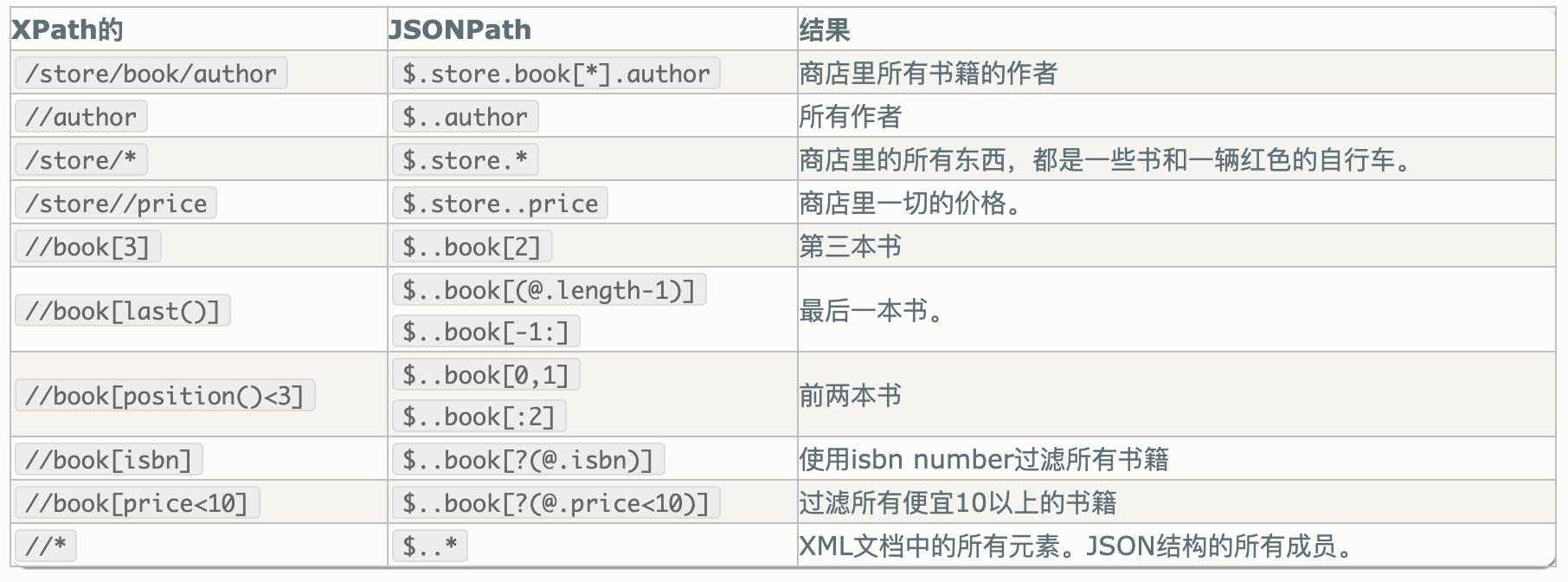
练习代码:
import jsonpath
info = {
"store": {
"book": [
{"category": "reference",
"author": "Nigel Rees",
"title": "Sayings of the Century",
"price": 8.95
},
{"category": "fiction",
"author": "Evelyn Waugh",
"title": "Sword of Honour",
"price": 12.99
},
{"category": "fiction",
"author": "Herman Melville",
"title": "Moby Dick",
"isbn": "0-553-21311-3",
"price": 8.99
},
{"category": "fiction",
"author": "J. R. R. Tolkien",
"title": "The Lord of the Rings",
"isbn": "0-395-19395-8",
"price": 22.99
}
],
"bicycle": {
"color": "red",
"price": 19.95
}
}
}
# 1. 提取第1本书的title
print("\n1. 提取第1本书的title")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$.store.book[0].title")
print(ret)
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$['store']['book'][0]['title']")
print(ret)
# 2. 提取2、3、4本书的标题
print("\n2. 提取2、3、4本书的标题")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$.store.book[1,2,3].title")
print(ret)
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$.store.book[1,2,3]['title']")
print(ret)
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$.store.book[1:4]['title']")
print(ret)
# 3. 提取1、3本书的标题
print("\n3. 提取1、3本书的标题")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$.store.book[::2].title")
print(ret)
# 4. 提取最后一本书的标题
print("\n4. 提取最后一本书的标题")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$.store.book[(@.length-1)].title")
print(ret)
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$.store.book[-1:].title")
print(ret)
# 5. 提取价格小于10的书的标题
print("\n5. 提取价格小于10的书的标题")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$.store.book[?(@.price < 10)].title")
print(ret)
# 6. 提取价格小于或者等于20的所有商品的价格
print("\n6. 提取价格小于或者等于20的所有商品的价格")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$..*[?(@.price <= 20)].price")
print(ret)
# 7. 获取所有书的作者
print("\n7. 获取所有书的作者")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$.store.book[::].author")
print(ret)
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$.store.book[*].author")
print(ret)
# 8. 获取所有作者
print("\n8. 获取所有作者")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$..author")
print(ret)
# 9. 获取在store中的所有商品(包括书、自行车)
print("\n9. 获取在store中的所有商品(包括书、自行车)")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$..store")
print(ret)
# 10. 获取所有商品(包括书、自行车)的价格
print("\n10. 获取所有商品(包括书、自行车)的价格")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$.store..price")
print(ret)
# 11. 获取带有isbn的书
print("\n11. 获取带有isbn的书")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$..book[?(@.isbn)]")
print(ret)
# 12. 获取不带有isbn的书
print("\n12. 获取不带有isbn的书")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$..book[?(!@.isbn)]")
print(ret)
# 13. 获取价格在5~10之间的书
print("\n13. 获取价格在5~10之间的书")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$..book[?(@.price>=5 && @.price<=10)]")
print(ret)
# 14. 获取价格不在5~10之间的书
print("\n13. 获取价格在5~10之间的书")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$..book[?(@.price<5 || @.price>10)]")
print(ret)
# 15. 获取所有的元素
print("\n15. 获取所有的元素")
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$..")
print(ret)
ret = jsonpath.jsonpath(info, "$..*")
print(ret)11.非结构化数据提取 - BS4
介绍与安装
介绍
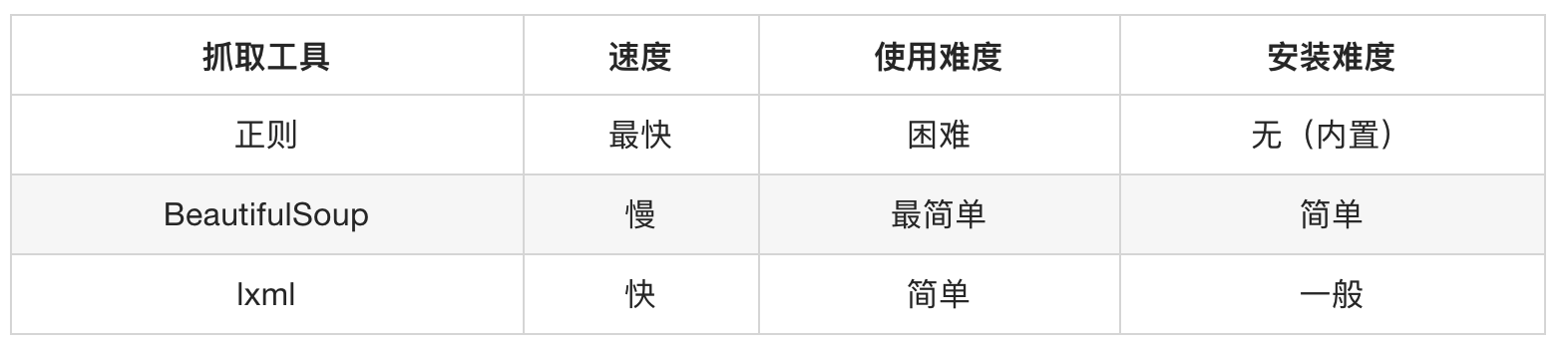
BeautifulSoup4简称BS4,和使用lxml模块 一样,Beautiful Soup 也是一个HTML/XML的解析器,主要的功能也是解析和提取HTML/XML数据。
Beautiful Soup是基于HTML DOM的,会载入整个文档,解析整个DOM树,因此时间和内存开销都会大很多,所以性能要低于lxml模块。
BeautifulSoup用来解析HTML比较简单,API非常人性化,支持CSS选择器、Python标准库中的HTML解析器,也支持 lxml模块的XML解析器
安装
pip install beautifulsoup4 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple官方文档:http://beautifulsoup.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/v4.4.0
BS4基本使用示例
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
# 创建 Beautiful Soup 对象
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
print(soup.prettify())搜索文档树中的标签、内容、属性
find_all方法中的参数
def find_all(self, name=None, attrs={}, recursive=True, string=None, limit=None, **kwargs)...
name参数
当前参数可以传递标签名称字符串,根据传递的标签名称搜索对应标签
# 1. 创建soup对象
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_obj, 'lxml')
# 2. 根据标签名称搜索标签
ret_1 = soup.find_all('b')
ret_2 = soup.find_all('a')
print(ret_1, ret_2)除了传递标签名称字符串之外也可传递正则表达式,如果传入正则表达式作为参数,Beautiful Soup会通过正则表达式的 match()来匹配内容。下面例子中找出所有以b开头的标签。
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_obj, 'lxml')
for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile('^b')):
print(tag.name)如果传递是一个列表,则Beautiful Soup会将与列表中任一元素匹配的内容返回。
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_obj, 'lxml')
ret = soup.find_all(['a', 'b'])
print(ret)
attrs参数:可以根据标签属性搜索对应标签
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
ret_1 = soup.find_all(attrs={'class': 'sister'})
print(ret_1)
print('-' * 30)
# 简写方式
ret_2 = soup.find_all(class_='sister')
print(ret_2)
print('-' * 30)
# 查询id属性为link2的标签
ret_3 = soup.find_all(id='link2')
print(ret_3)
string参数:通过string参数可以搜索文档中的字符串内容,与name参数的可选值一样,string参数接受字符串 , 正则表达式 , 列表
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
ret_1 = soup.find_all(string='Elsie')
print(ret_1)
ret_2 = soup.find_all(string=['Tillie', 'Elsie', 'Lacie'])
print(ret_2)
ret_3 = soup.find_all(string=re.compile('Dormouse'))
print(ret_3)
find方法
find的用法与find_all一样,区别在于find返回第一个符合匹配结果,find_all则返回所有匹配结果的列表
搜索文档树中的css选择器
另一种与find_all方法有异曲同工之妙的查找方法,也是返回所有匹配结果的列表。
css选择器编写注意事项:
- 标签名称不加任何修饰
- 类名前加
. id属性名称前加#
css选择器编写方式与编写css样式表的语法大致相同。在bs4中可以直接使用soup.select()方法进行筛选,返回值类型是一个列表。
标签选择器
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
print(soup.select('title'))
print(soup.select('a'))
print(soup.select('b'))类选择器
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
print(soup.select('.sister'))
id选择器
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
print(soup.select('#link1'))层级选择器
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
print(soup.select('p #link1'))属性选择器
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
print(soup.select('a[class="sister"]'))
print('-' * 30)
print(soup.select('a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]'))
get_text()方法:获取文本内容
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
# select返回的是列表对象, 需要使用for循环遍历列表元素再使用get_text方法获取文本数据
for title in soup.select('title'):
print(title.get_text())
get()方法:获取属性
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
for attr in soup.select('a'):
print(attr.get('href'))总结
- 安装
beautifulsoup4:pip install beautifulsoup4 beautifulsoup导包:from bs4 import BeautifulSoupbeautifulsoup转换类型:BeautifulSoup(html)find方法返回一个解析完毕的对象findall方法返回的是解析列表listselect方法返回的是解析列表list- 获取属性的方法:
get('属性名字') - 和获取文本的方法:
get_text()
12.练习:使用BS4抓取搜狗微信下的所有文章标题
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = "https://weixin.sogou.com/weixin?_sug_type_=1&type=2&query=python"
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_3) "
"AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/86.0.4240.183 Safari/537.36"
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers).text
soup = BeautifulSoup(response, 'lxml')
ul_tag = soup.select('ul[class="news-list"]')
# print(ul_tag)
h3_list = ul_tag[0].select('h3')
for temp in h3_list:
print(temp.select('a')[0].get_text(), temp.select('a')[0].get('href'))
print('-' * 30)